Explanation:
Both triangles, being right-angled and isosceles, have 2 sides equal and a pair of 45° angles each.
Consider the triangle to the left, the fact that the square has 4 right angles will enable us to find the angles of the smaller triangles within the main triangle. Already knowing that one of the angles is equal to 45°, combined with the knowledge that we now have a right angle, means that the third angle is 45°. This applies to both smaller triangles. Because we have 2 base angles equal, we can deduce that the smaller triangles are also right-angled and isosceles. Knowing that each side of the square is 21 cm allows us to find the other side of the smaller isosceles triangles, also being 21. Consequently, we will be able to determine that the equal sides of the main right-angled isosceles triangle are 42 cm.
With this knowledge, we can now find the length of the hypotenuse. Using the Pythagoras theorem:
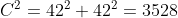
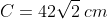
Moving on to the triangle on the right, determining the value of all the angles will enable us to progress towards finding the answer. Since it is given that both triangles are congruent, we know that all their dimensions (sides and angles) are equal. Similar to the triangle to the left, having an inscribed square in the main triangle means that there is also a right angle in 2 smaller triangles. With the given knowledge that the base angles of the main triangle are equal to 45°, we can determine the value of the third angle, which is also 45°. This means that both smaller triangles are also right-angled and isosceles. Since there are three sides belonging to the smaller triangles and the inscribed square on the hypotenuse, and with all of those sides being equal, we can now calculate the length of the side of the square inscribed into the triangle to the right, as follows:
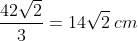 Figures with all known data:
Figures with all known data:
I hope this helps!
