I agree with Eagle Mum about the equation that was likely intended, but I don't agree about the answer.
Adding water will (theoretically) lead to a shift right (applying Le Chatelier's Principle), but water being the solvent and effectively constant in concentration means adding it has little practical effect. Further, the addition of water would dilute all of the species, decreasing the concentration of both reactants and products.
I believe the best answer is (B) and I would expect that to be the only accepted answer if the equation suggested above was given. The reason is that adding hydrochloric acid would neutralise some of the hydroxide ion, decreasing the concentration of a product and thus causing a shift to the right by applying Le Chatelier's Principle.
The usual approach to MCQ is that the
best answer should be given and (B) is unambiguously going to cause an increase in the concentration of HOCl. If water is added and causes a shift to the right, the overall effect could still be a decrease in the concentration of HOCl due to the dilution. That is, we could have:
- [HOCl] is x mol/L
- Water is added, causing [HOCl] to instantly fall to (say) 0.8x mol/L
- The shift to the right in line with Le Chatelier's Principle causes more HOCl to be produced
- Hence, [HOCl] rises back to 0.95x mol/L
I am making these numbers up but they illustrate that the concentration could fall (overall) while rising due to the shift under a scenario from answer (A).
PS: What made me notice the unbalanced equation was considering answer (C). If the equation did include HCl which, being a strong acid, would be ionised to H
+ and Cl
-, then adding KCl (and hence a source of chloride ions) could cause a shift the the right. So...
- (D) would cause a shift left by adding hydroxide ions, a product
- (C) would have no effect if the equation has no potassium ions or chloride ions, or a shift right with the unbalanced equation given.
- (B) would cause a shift right in the equation as written by adding a reactant and consuming a product (which illustrates that the equation given is strange), and would cause a shift right for the (likely) intended equation by removal of hydroxide ions, a product
- (A) is meant to be treated as having no effect, being a solvent in a case where it does not appear in the equation (Suppose enough water is added to halve the concentration of every species in the equation given... the value of Q would not change as [C][D] / [A][
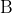 ] would become ([C] / 2)([D] / 2) / ([A] / 2)([
] would become ([C] / 2)([D] / 2) / ([A] / 2)([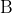 ] / 2), which has the same value.) If water is a reactant, as in the (likely) intended equation, Le Chatelier's Principle says shift right but the disturbance has changed the concentration of all of the species and may cause all species concentrations to fall overall.
] / 2), which has the same value.) If water is a reactant, as in the (likely) intended equation, Le Chatelier's Principle says shift right but the disturbance has changed the concentration of all of the species and may cause all species concentrations to fall overall.
